Introduction of Multi-Currency Expert Advisor.
While this article focuses on the Three Moving Average Crossover, it is important to note that the implementation of a multi-currency expert advisor follows the same principles and templates as outlined in my previous articles. For a detailed guide on creating a multi-currency expert advisor, you can refer to the following resources:
How to create a simple Multi-Currency Expert Advisor using MQL5 with Zigzag and RSI Indicators Signal: This article provides a comprehensive guide on building a multi-currency expert advisor using MQL5, leveraging Zigzag and RSI indicators for signal generation. The step-by-step approach ensures you can easily adapt these techniques for various trading strategies.
How to create a FiboPivotCandleBar Expert Advisor that trades Multi-Currency for MT5: In this article, I explain how to create a multi-currency expert advisor using the FiboPivotCandleBar indicator. The focus is on integrating the indicator into your trading strategy and automating the process for multiple currency pairs.
A Comprehensive Guide to FiboPivotCandleBar: Functions and Performance of the Expert Advisor for MT5: This comprehensive guide dives into the functions and performance of the FiboPivotCandleBar expert advisor, offering insights into its effectiveness and how to optimize it for multi-currency trading.
By following the principles and templates provided in these articles, we can effectively create and implement a multi-currency expert advisor that incorporates the Three Moving Average Crossover strategy.
Introduction the Three Moving Average Crossover Strategy in Forex Trading
What is a moving average?
- "A moving average is a simple technical analysis tool that helps smooth out pricedata by creating a constantly updated average price. It is calculated by adding up a certain number of closing prices and then dividing this total by that number."
- Moving averages are a type of technical analysis tool that smooths out price data to create a trend-following indicator. There are four main types of moving averages:
- 1. Simple Moving Average (SMA)
- The Simple Moving Average (SMA) is the most basic type of moving average. It is calculated by adding up the closing prices of an asset over a specific number of periods and then dividing the total by that number of periods. The SMA gives equal weight to each price point within the chosen period.
- Formula: SMA = (P1 + P2 + ... + Pn) / n. Where P represents the closing prices and n is the number of periods. Where 𝑃 represents the closing prices and 𝑛 is the number of periods.
- Usage: The SMA is commonly used to identify trend directions and potential support and resistance levels. It is straightforward and easy to understand, making it popular among traders.
- 2. Exponential Moving Average (EMA)
- The Exponential Moving Average (EMA) gives more weight to recent prices, making it more responsive to new information. Unlike the SMA, the EMA reacts more quickly to price changes because it applies a smoothing factor to give more importance to recent data points.
- Formula: EMA = [(Pt - EMAy) / (k + 1)] + EMAy. Where Pt is the current price, EMAy is the previous EMA value, and k is the smoothing factor which depends on the number of periods.
- Usage: The EMA is preferred by traders who want to capture trends faster and more accurately. It is useful for identifying short-term trading opportunities and trend reversals.
- 3. Smoothed Moving Average (SMMA)
- The Smoothed Moving Average (SMMA) is a combination of the SMA and the EMA. It provides a smoother line by reducing the noise from random price fluctuations. The SMMA calculates an average similar to the SMA but applies a smoothing factor, which decreases the influence of past prices gradually.
- Formula: SMMA = [(SMMAprevious * (n - 1)) + Pt] / n. Where SMMAprevious is the previous smoothed average, Pt is the current price, and n is the number of periods.
- Usage: The SMMA is ideal for traders looking for a smoother trend line that filters out volatility. It is often used in longer-term trend analysis.
- 4. Linear Weighted Moving Average (LWMA)
- The Linear Weighted Moving Average (LWMA) assigns more weight to recent prices while giving progressively less weight to older prices. This is achieved by multiplying each price point by a weight that decreases linearly from the most recent price to the oldest within the selected period.
- Formula: LWMA = [Σ(Pi * i)] / [Σi]. Where Pi is the price at period i and n is the number of periods.
- Usage: The LWMA is used by traders who want to place a stronger emphasis on recent price actions. It is useful for detecting short-term price movements and trends.
Why moving average crossovers are popular?
- Moving average crossovers are a popular trading strategy because they provide clear signals to buy or sell an asset. When a short-term moving average crosses above a long-term moving average, it often signals a bullish trend, and viceversa.
- In the world of forex trading, the Moving Average Crossover strategy is a popular and effective tool used by both beginners and experienced traders. This strategy involves the use of two or more different moving averages to identify potential buying and selling opportunities in the market. In this article, we will explore the basics of the Moving Average Crossover strategy, how it works, and tips for maximizing its effectiveness.
Introduction:
The Triple Moving Average Crossover strategy is a powerful tool used by forex traders to identify potential trading opportunities. By employing three moving averages with different periods, this strategy aims to increase the accuracy of signals and minimize the chances of false breakouts. In this article, we will delve into the details of this strategy, explaining how it works and how traders can use it to enhance their trading decisions.
Moving Averages Used
In the Triple Moving Average Crossover strategy, three moving averages are utilized:
- Slow MA: 30-period Smoothed Moving Average (SMMA) using the median price. This moving average helps to identify the overall long-term trend.
- Middle MA: 20-period Simple Moving Average (SMA) using the median price. This moving average acts as a filter to smooth out price fluctuations.
- Fast MA: 2-period Simple Moving Average (SMA) using the typical price. This moving average responds quickly to price changes, providing early signals for potential trades.
Buy Signals
The strategy generates buy signals based on the interaction of the three moving averages:
- 1. Signal Up 1: A buy signal is generated when the Fast MA (2-period) crosses above the Slow MA (30-period), and the Middle MA (20-period) is below the Slow MA. This indicates the potential start of an uptrend.
Example: If the Fast MA (2) moves from below to above the Slow MA (30), and the Middle MA (20) remains below the Slow MA, it suggests a bullish signal. - 2. Signal Up 2: Another buy signal occurs when the Middle MA (20-period) crosses above the Slow MA (30-period), and the Fast MA (2-period) subsequently crosses above the Middle MA. This confirms the continuation of the uptrend.
Example: If the Middle MA (20) is above the Slow MA (30) and the Fast MA (2) crosses from below to above the Middle MA (20), it indicates a strong bullish signal.
Sell Signals
Similarly, the strategy generates sell signals when the moving averages align in the opposite direction:
- 1. Signal Down 1: A sell signal is generated when the Fast MA (2-period) crosses below the Slow MA (30-period), and the Middle MA (20-period) is above the Slow MA. This suggests the potential start of a downtrend.
Example: If the Fast MA (2) moves from above to below the Slow MA (30), and the Middle MA (20) remains above the Slow MA, it signals a bearish trend. - 2. Signal Down 2: Another sell signal occurs when the Middle MA (20-period) crosses below the Slow MA (30-period), and the Fast MA (2-period) subsequently crosses below the Middle MA. This confirms the continuation of the downtrend.
Example: If the Middle MA (20) is below the Slow MA (30) and the Fast MA (2) crosses from above to below the Middle MA (20), it indicates a strong bearish signal.
Let's break down the ExpMACross1_MCEA_Config function of ExpMACross1_MCEA Expert Advisor for MT5.
void MCEA::ExpMACross1_MCEA_Config(void)
This function configures the Moving Average Crossover strategy and configures various elements. It sets up the timeframes, moving averages, and various parameters for the trading strategy, such as handling symbol arrays, setting up the moving averages for different timeframes, and configuring risk management settings like stop-loss and take-profit levels.
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+
//| Expert Configuration |
//+------------------------------------------------------------------+
void MCEA::ExpMACross1_MCEA_Config(void)
{
//---
//--
HandlingSymbolArrays(); // With this function we will handle all pairs that will be traded
//--
TFT05=PERIOD_M5;
ENUM_TIMEFRAMES TFs[]={PERIOD_M5,PERIOD_M15,PERIOD_M30,PERIOD_H1,PERIOD_H2,PERIOD_H3,PERIOD_H4,PERIOD_H6,PERIOD_H8,PERIOD_H12,PERIOD_D1};
int arTFs=ArraySize(TFs);
//--
for(int x=0; x<arTFs; x++) if(tfinuse==x) TFt=TFs[x]; // TF for calculation signal
//--
int SMMAL=30;
int SMAMi=20;
int SMAKc=2;
//-- Indicators handle for all symbol
//TesterHideIndicators(true);
//--
for(int x=0; x<arrsymbx; x++)
{
hSMMAL[x]=iMA(DIRI[x],TFt,SMMAL,0,MODE_SMMA,PRICE_MEDIAN); //-- Handle for the Slow MA indicator
hSMAMi[x]=iMA(DIRI[x],TFt,SMAMi,0,MODE_SMA,PRICE_MEDIAN); //-- Handle for the Middle MA indicator
hSMAKc[x]=iMA(DIRI[x],TFt,SMAKc,0,MODE_SMA,PRICE_TYPICAL); //-- Handle for the Fast MA indicator
hPar05[x]=iSAR(DIRI[x],TFT05,SARstep,SARmaxi); //-- Handle for the iSAR indicator for M5 Timeframe
//--
}
//--
minprofit=NormalizeDouble(TSmin/100.0,2);
//--
ALO=(int)mc_account.LimitOrders()>sall ? sall : (int)mc_account.LimitOrders();
if(Close_by_Opps==No)
{
if((int)mc_account.LimitOrders()>=(sall*2)) ALO=sall*2;
else
ALO=(int)(mc_account.LimitOrders()/2);
}
//--
LotPS=(double)ALO;
maxSpread=maxsprd;
if(MQLInfoInteger(MQL_TESTER))
maxSpread=(int)SymbolInfoInteger(Symbol(),SYMBOL_SPREAD);
//--
valSL=TSval==0.0 ? 38.0 : TSval;
valTP=TPval==0.0 ? 35.0 : TPval;
minSL=TSmin==0.0 ? 5.0 : TSmin;
minTP=TPmin==0.0 ? 25.0 : TPmin;
//--
mc_trade.SetExpertMagicNumber(magicEA);
mc_trade.SetDeviationInPoints(slip);
mc_trade.SetMarginMode();
Set_Time_Zone();
//--
return;
//---
} //-end ExpMACross1_MCEA_Config()
//---------//
- Indicator Handles for Each Pair
- In this EA, indicator handles are created for each symbol (pair) that intend to trade. This setup allows the EA to calculate and use indicators specifically for each pair. Let's go through the setup step-by-step:
- 1. Handling Symbol Arrays: This function initializes and handles all the symbols that will be traded. It ensures the EA has access to the required symbols.
- 2. Indicator Handles Setup: For each symbol, the EA creates handles for the moving averages (Slow, Middle, Fast) and the SAR indicator. Here's how it's done:
//-- for(int x=0; x<arrsymbx; x++) { //-- Handle for the Slow MA indicator hSMMAL[x]=iMA(DIRI[x],TFt,SMMAL,0,MODE_SMMA,PRICE_MEDIAN); //-- Handle for the Middle MA indicator hSMAMi[x]=iMA(DIRI[x],TFt,SMAMi,0,MODE_SMA,PRICE_MEDIAN); //-- Handle for the Fast MA indicator hSMAKc[x]=iMA(DIRI[x],TFt,SMAKc,0,MODE_SMA,PRICE_TYPICAL); //-- Handle for the iSAR indicator for M5 Timeframe hPar05[x]=iSAR(DIRI[x],TFT05,SARstep,SARmaxi); //-- } //-- - 3. Explanation of Each Handle:
- hSMMAL[x]: This handle is used to calculate the Slow Moving Average (SMMA) for each symbol. It uses a 30-period setting with the median price (PRICE_MEDIAN).
- hSMAMi[x]: This handle calculates the Middle Moving Average (SMA) for each symbol. It uses a 20-period setting with the median price (PRICE_MEDIAN).
- hSMAKc[x]: This handle calculates the Fast Moving Average (SMA) for each symbol. It uses a 2-period setting with the typical price (PRICE_TYPICAL).
- hPar05[x]: This handle calculates the Parabolic SAR indicator for each symbol. It uses specific SAR step and maximum values and is set for the M5 timeframe.
- 4. Using the Handles in the EA: These handles are used within the EA to perform calculations and make trading decisions based on the Moving Average Crossover strategy. The EA monitors the crossovers of these moving averages to generate buy or sell signals for each symbol.
By setting up these indicator handles for each pair, the EA can accurately calculate the necessary values and generate trading signals for all the symbols in the multi-currency strategy, including XAUUSD and XAGUSD.
Let's break down the ExpertActionTrade function to understand its various components and their purposes.
void MCEA::ExpertActionTrade(void)
{
//---
//--Check Trading Terminal
ResetLastError();
//--
if(!DisplayManualButton("M","C","R")) DisplayManualButton(); //-- Show the expert manual button panel
//--
if(trade_info_display==Yes) mc.TradeInfo(); //-- Displayed Trading Info on Chart
//---
if(!MQLInfoInteger(MQL_TRADE_ALLOWED) && mc.checktml==0) //-- Check whether MT5 Algorithmic trading is Allow or Prohibit
{
mc.Do_Alerts(Symbol(),"Trading Expert at "+Symbol()+" are NOT Allowed by Setting.");
mc.checktml=1; //-- Variable checktml is given a value of 1, so that the alert is only done once.
return;
}
//--
//---
int mcsec=mc.ThisTime(mc.sec);
//--
if(fmod((double)mcsec,5.0)==0) mc.ccur=mcsec;
//--
if(mc.ccur!=mc.psec)
{
string symbol;
//-- Here we start with the rotation of the name of all symbol or pairs to be traded
for(int x=0; x<mc.arrsymbx && !IsStopped(); x++)
{
//--
switch(trademode)
{
case SP:
{
if(mc.DIRI[x]!=Symbol()) continue;
symbol=Symbol();
break;
}
case MP:
{
if(mc.DIRI[x]==Symbol()) symbol=Symbol();
else symbol=mc.DIRI[x];
break;
}
}
//--
mc.CurrentSymbolSet(symbol);
//--
if(mc.TradingToday() && mc.Trade_session())
{
//--
mc.OpOr[x]=mc.GetOpenPosition(symbol); //-- Get trading signals to open positions
//-- //-- and store in the variable OpOr[x]
if(mc.OpOr[x]==mc.Buy) //-- If variable OpOr[x] get result of GetOpenPosition(symbol) as "Buy" (value=1)
{
//--
mc.CheckOpenPMx(symbol);
//--
if(Close_by_Opps==Yes && mc.xos[x]>0) mc.CloseSellPositions(symbol);
//--
if(mc.xob[x]==0 && mc.xtto<mc.ALO && mc.IFNewBarsB(symbol)) {mc.OpenBuy(symbol); mc.PbarB[x]=mc.TbarB[x];}
else
if(mc.xtto>=mc.ALO)
{
//--
mc.Do_Alerts(symbol,"Maximum amount of open positions and active pending orders has reached"+
"n the limit = "+string(mc.ALO)+" Orders ");
//--
mc.CheckOpenPMx(symbol);
//--
if(mc.xos[x]>0 && mc.profits[x]<-1.02 && mc.xob[x]==0) {mc.CloseSellPositions(symbol); mc.OpenBuy(symbol);}
else
mc.CloseAllProfit();
}
}
if(mc.OpOr[x]==mc.Sell) //-- If variable OpOr[x] get result of GetOpenPosition(symbol) as "Sell" (value=-1)
{
//--
mc.CheckOpenPMx(symbol);
//--
if(Close_by_Opps==Yes && mc.xob[x]>0) mc.CloseBuyPositions(symbol);
//--
if(mc.xos[x]==0 && mc.xtto<mc.ALO && mc.IFNewBarsS(symbol)) {mc.OpenSell(symbol); mc.PbarS[x]=mc.TbarS[x];}
else
if(mc.xtto>=mc.ALO)
{
//--
mc.Do_Alerts(symbol,"Maximum amount of open positions and active pending orders has reached"+
"n the limit = "+string(mc.ALO)+" Orders ");
//--
mc.CheckOpenPMx(symbol);
//--
if(mc.xob[x]>0 && mc.profitb[x]<-1.02 && mc.xos[x]==0) {mc.CloseBuyPositions(symbol); mc.OpenSell(symbol);}
else
mc.CloseAllProfit();
}
}
}
//--
mc.CheckOpenPMx(symbol);
//--
if(mc.xtto>0)
{
//--
if(SaveOnRev==Yes) //-- Close Trade and Save profit due to weak signal (Yes)
{
mc.CheckOpenPMx(symbol);
if(mc.profitb[x]>mc.minprofit && mc.xob[x]>0 && mc.GetCloseInWeakSignal(symbol,mc.Buy)==mc.Sell)
{
mc.CloseBuyPositions(symbol);
mc.Do_Alerts(symbol,"Close BUY order "+symbol+" to save profit due to weak signal.");
}
if(mc.profits[x]>mc.minprofit && mc.xos[x]>0 && mc.GetCloseInWeakSignal(symbol,mc.Sell)==mc.Buy)
{
mc.CloseSellPositions(symbol);
mc.Do_Alerts(symbol,"Close SELL order "+symbol+" to save profit due to weak signal.");
}
}
//--
if(UseTCP==Yes) mc.CheckTargetCloseProfit();
//--
if(TrailingSL==Yes) mc.ModifyOrdersSL(symbol,trlby); //-- Use Trailing Stop Loss (Yes)
if(TrailingTP==Yes) mc.ModifyOrdersTP(symbol); //-- Use Trailing Take Profit (Yes)
//--
}
//--
mc.CheckOpenPMx(symbol);
if(Close_by_Opps==No && (mc.xob[x]+mc.xos[x]>1))
{
mc.CheckProfitLoss(symbol);
mc.Do_Alerts(symbol,"Close order due stop in loss.");
}
//--
mc.CheckClose(symbol);
}
//--
mc.psec=mc.ccur;
}
//--
return;
//---
} //-end ExpertActionTrade()
//---------//
ExpertActionTrade Function Explanation.
1. Check Trading Terminal:
- Resets any previous errors to ensure fresh error checking.
- Displays manual button panel for user interaction.
- Displays trading info on the chart if enabled.
2. Check MT5 Algorithmic Trading Status:
- Checks if algorithmic trading is allowed. If not, alerts the user and stops further execution.
3. Time Management:
- Manages the timing of the function to ensure it runs at the correct intervals.
4. Symbol Rotation:
- Rotates through all symbols (pairs) that will be traded. Handles single pair (SP) and multi-pair (MP) trading modes.
5. Trading Logic:
- Checks if trading is allowed today and if the trading session is active.
- Gets trading signals to open positions and executes buy/sell orders based on the signals.
- Manages open positions, ensures that the maximum allowed positions are not exceeded, and handles closing positions based on profit or weak signals.
6. Risk and Trade Management:
- Manages trailing stop loss and trailing take profit.
- Ensures that weak signal positions are closed to save profit.
- Checks and closes orders if they hit the stop-loss limit.
7. Final Checks and Cleanup:
- Ensures all checks are made and closes positions if necessary.
- Returns control back to the main program.
This function encapsulates the entire trading logic, from checking if trading is allowed, processing signals, executing trades, and managing risk. It operates on multiple symbols (pairs) and ensures that trading decisions are made based on the configured strategy and risk management rules.
Let's break down the GetOpenPosition function to understand its components and their purposes:
int MCEA::GetOpenPosition(const string symbol) // Signal Open Position
{
//---
int ret=0;
int rise=1,
down=-1;
//--
int SMAC=SignalMACross1(symbol);
int DirM=DirectionMove(symbol,TFt);
//--
if(SMAC==rise && DirM==rise) ret=rise;
if(SMAC==down && DirM==down) ret=down;
//--
return(ret);
//---
} //-end GetOpenPosition()
//---------//
GetOpenPosition Function Explanation
This function determines the signal for opening a position (buy or sell) based on the Moving Average Crossover strategy and the direction of the market.
1. Initialize Variables:
ret:This variable will store the result, indicating the type of position to open (buy or sell). It is initialized to0.riseanddown: These constants represent the direction of the trade.riseis set to1(indicating a buy signal), anddownis set to-1(indicating a sell signal).
2. Get Signals:
SMAC:This variable stores the result of theSignalMACross1function, which checks for moving average crossovers and returns a signal (riseordown).DirM:This variable stores the result of theDirectionMovefunction, which determines the overall market direction for the given timeframe (TFt).
3. Determine Open Position Signal:
- If both the moving average crossover signal (
SMAC) and the market direction (DirM) indicate a rise (both equal torise), the function setsrettorise, indicating a buy signal. - If both
SMACandDirMindicate a downtrend (both equal todown), the function setsrettodown, indicating a sell signal.
4. Return the Result:
- The function returns the value of
ret, which indicates whether to open a buy position (1), a sell position (-1), or no position (0).
Summary
The GetOpenPosition function integrates the results from the moving average crossover signal and the market direction to generate a coherent trading signal. If both indicators agree on the direction (either up or down), the function returns the corresponding signal to open a buy or sell position. Otherwise, it returns 0, indicating no position should be opened.
Let's break down the SignalMACross1 function to understand how it determines the moving average crossover signals:
nt MCEA::SignalMACross1(const string symbol)
{
//---
int ret=0;
int rise=1,
down=-1;
//--
double BMAL[],
BMAM[],
BMAK[];
//--
ArrayResize(BMAL,arper,arper);
ArrayResize(BMAM,arper,arper);
ArrayResize(BMAK,arper,arper);
//--
int xm=PairsIdxArray(symbol);
UpdatePrice(symbol,TFt);
//--
CopyBuffer(hSMMAL[xm],0,0,arper,BMAL);
CopyBuffer(hSMAMi[xm],0,0,arper,BMAM);
CopyBuffer(hSMAKc[xm],0,0,arper,BMAK);
//--
ArraySetAsSeries(BMAL,true);
ArraySetAsSeries(BMAM,true);
ArraySetAsSeries(BMAK,true);
//--
bool SigMAup1=(BMAK[1]<=BMAL[1] && BMAK[0]>BMAL[0] && BMAM[0]<BMAL[0]);
bool SigMAdw1=(BMAK[1]>=BMAL[1] && BMAK[0]<BMAL[0] && BMAM[0]>BMAL[0]);
//--
bool SigMAup2=(BMAM[0]>BMAL[0] && BMAK[1]<=BMAM[1] && BMAK[0]>BMAM[0]);
bool SigMAdw2=(BMAM[0]<BMAL[0] && BMAK[1]>=BMAM[1] && BMAK[0]<BMAM[0]);
//--
int PPMv=PricePercentMove(symbol,TFt,10.0,0);
//--
if((SigMAup1||SigMAup2) && PPMv==rise) ret=rise;
if((SigMAdw1||SigMAdw2) && PPMv==down) ret=down;
//--
return(ret);
//---
} //-end SignalMACross1()
//---------//
SignalMACross1 Function Explanation
This function checks for moving average crossovers and determines the trading signal based on these crossovers and the price movement.
- 1. Initialize Variables:
- ret: This variable will store the result, indicating the type of signal (buy or sell). It is initialized to 0.
- rise and down: These constants represent the direction of the trade. rise is set to 1 (indicating a buy signal), and down is set to -1 (indicating a sell signal).
- 2. Declare Buffers for Moving Averages:
- BMAL, BMAM, BMAK: These arrays will store the values of the Slow, Middle, and Fast moving averages, respectively.
- 3. Resize Arrays:
- Resizes the arrays to accommodate the required number of periods (arper).
- 4. Get Index and Update Prices:
- xm: Gets the index of the symbol in the pairs array.
- Updates the price data for the specified timeframe (TFt).
- 5. Copy Indicator Buffers:
- Copies the buffer values of the Slow, Middle, and Fast moving averages into the respective arrays.
- 6. Set Arrays as Series:
- Sets the arrays to work as series, where the most recent data is at index 0.
- 7. Determine Crossover Signals:
- Signal Up 1: Checks if the Fast MA crosses above the Slow MA and the Middle MA is below the Slow MA.
- Signal Down 1: Checks if the Fast MA crosses below the Slow MA and the Middle MA is above the Slow MA.
- Signal Up 2: Checks if the Middle MA is above the Slow MA and the Fast MA crosses above the Middle MA.
- Signal Down 2: Checks if the Middle MA is below the Slow MA and the Fast MA crosses below the Middle MA.
- 8. Check Price Movement:
- PPMv: Calls the PricePercentMove function to check the price movement direction.
- 9. Determine Final Signal:
- If any of the "up" signals are true and the price movement indicates a rise, set ret to rise.
- If any of the "down" signals are true and the price movement indicates a downtrend, set ret to down.
- 10. Return the Result:
- The function returns the value of ret, indicating whether to generate a buy signal (1), a sell signal (-1), or no signal (0).
Summary
The SignalMACross1 function checks for specific moving average crossovers and determines the trading signal based on these crossovers and the overall price movement. It ensures that the signals are consistent with the market direction before returning the appropriate trading signal.
Let's break down the PricePercentMove function to understand its components and their purposes:
PricePercentMove Function Explanation
- 1. Initialize Variables:
- ret: This variable will store the result, indicating the direction of the price movement. It is initialized to 0.
- rise and down: These constants represent the direction of the trade. rise is set to 1 (indicating a price rise), and down is set to -1 (indicating a price fall).
- 2. Setup for Calculation:
- br: The number of bars (periods) to be considered, set to shift + 3.
- hasil: A variable to store the calculated result of the price movement.
- move: The threshold percentage move to consider for the direction.
- 3. Update Prices:
- Updates the price data for the specified symbol and timeframe.
- 4. Declare and Resize Array for Close Prices:
- CL: An array to store the close prices.
- Resizes the array to the number of bars (br) and sets it as a series (most recent data at index 0).
- 5. Copy Close Prices:
- Copies the close prices into the array CL for the specified number of bars.
- 6. Calculate Price Movement:
- close_now: The most recent close price.
- close_prev: The previous close price.
- Calculates the percentage change in price between the two close prices. If either price is 0 or EMPTY_VALUE, sets hasil to 0.0. Otherwise, normalizes the percentage change and adjusts it to be a more readable percentage.
- 7. Determine Direction:
- If the percentage move hasil is greater than the threshold move, sets ret to rise.
- If hasil is less than the negative of move, sets ret to down.
- 8. Return the Result:
- The function returns the value of ret, indicating whether the price has risen (1), fallen (-1), or remained within the threshold (0)
Summary
The PricePercentMove function calculates the percentage change in the closing prices of a symbol over a specified period and timeframe. It then determines whether the price has risen, fallen, or remained relatively unchanged based on a specified threshold percentage (pcm). This information is used to identify the direction of the price movement and generate appropriate trading signals.
Let's break down the DirectionMove function to understand how it determines the direction of the bar price movement:
DirectionMove Function Explanation
This function calculates the direction of the price movement of a specific bar in a given timeframe, and returns whether the price is rising or falling.
- 1. Initialize Variables:
- ret: This variable will store the result, indicating the direction of the price movement. It is initialized to 0.
- rise and down: These constants represent the direction of the price movement. rise is set to 1 (indicating a price rise), and down is set to -1 (indicating a price fall).
- 2. Calculate Pips:
- Calls the Pips function to set the pip value for the symbol.
- 3. Normalize Price Difference:
- difud: Calculates the normalized price difference using mc_symbol.NormalizePrice and 1.5 * pip. This threshold is used to determine significant price movements.
- 4. Update Prices:
- Updates the price data for the specified symbol and timeframe.
- 5. Determine Price Direction:
- Checks if the closing price of the current bar (CLOSE[0]) is greater than the opening price plus the threshold (OPEN[0] + difud). If true, sets ret to rise.
- Checks if the closing price of the current bar (CLOSE[0]) is less than the opening price minus the threshold (OPEN[0] - difud). If true, sets ret to down.
- 6. Return the Result:
- The function returns the value of ret, indicating whether the price has risen (1), fallen (-1), or remained within the threshold (0).
Summary
The DirectionMove function calculates the direction of the price movement for a specific bar in a given timeframe. It does this by comparing the closing price to the opening price, with a threshold to filter out insignificant movements. The function returns whether the price is rising, falling, or remains within a negligible range.
Let's break down the GetCloseInWeakSignal function to understand its components and how it determines whether to close a position based on weak signals:
GetCloseInWeakSignal Function Explanation
This function determines if a position should be closed based on weak signals from moving averages, direction, and price percent move.
- 1. Initialize Variables:
- ret: This variable will store the result, indicating whether to close the position. It is initialized to 0.
- rise and down: These constants represent the direction. rise is set to 1, and down is set to -1.
- bar: The number of bars to consider, set to 5.
- x: The index of the symbol in the pairs array.
- 2. Declare and Resize Array for Fast MA:
- BMAK: An array to store the values of the Fast Moving Average.
- Resizes the array to bar size and copies the buffer values of the Fast MA into the array.
- 3. Set Array as Series:
- Sets the array BMAK to work as a series, where the most recent data is at index 0.
- 4. Determine Fast MA Direction:
- BMKup: Checks if the Fast MA is moving up (current value is greater than the previous value).
- BMKdw: Checks if the Fast MA is moving down (current value is less than the previous value).
- 5. Get Direction and Price Percent Move:
- DirM: Calls the DirectionMove function to get the direction of the bar price.
- PPmv: Calls the PricePercentMove function to get the price percent move.
- 6. Determine Close Signal:
- If the existing position (exis) is a sell (down), and the direction (DirM), price percent move (PPmv), and Fast MA (BMKup) all indicate a rise, sets ret to rise.
- If the existing position (exis) is a buy (rise), and the direction (DirM), price percent move (PPmv), and Fast MA (BMKdw) all indicate a fall, sets ret to down.
- 7. Return the Result:
- The function returns the value of ret, indicating whether to close the position (rise or fall) based on weak signals.
Summary
The GetCloseInWeakSignal function checks for weak signals based on the Fast Moving Average direction, bar price direction, and price percent move. If the weak signals indicate that the market is moving against the existing position, it returns a signal to close the position.
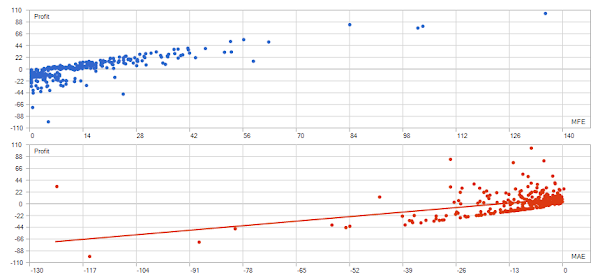
Backtesting Period: December 2, 2024 - December 20, 2024
I have backtested this strategy from December 1, 2024, to December 20, 2024. I chose this period because, typically, December experiences highly volatile and even sideways market conditions. If a strategy is not robust, it is likely to incur losses during this time. The Expert Advisor (EA) I developed is a multi-currency EA, covering 28 currency pairs and 2 metal pairs (XAUUSD and XAGUSD).
The backtesting of the Triple Moving Average Crossover strategy was conducted from December 2, 2024, to December 20, 2024, across various currency pairs and metals. The following is a summary of the key performance metrics:
Visual Analysis:
The backtesting results provide a comprehensive summary of the performance of the Triple Moving Average Crossover strategy:
- Balance and Equity Lines: The balance (in blue) and equity (in green) lines show the overall performance, with the balance line generally trending upwards with fluctuations. The equity line exhibits more volatility but also an upward trend.
- Deposit Load: The bar chart below the main graph indicates varying levels of deposit load throughout the period, reflecting the percentage of the deposit being utilized.
- Drawdown: The maximum balance drawdown was 2.15%, reflecting a relatively low risk level. The equity drawdown was slightly higher at 3.51%.
These visual elements provide a clear representation of the strategy's performance, illustrating both profit opportunities and risk levels.
Detailed Analysis:
- Strategy Performance
- The strategy yielded a total profit of $675.43 with a profit factor of 1.38, indicating that the total profits exceeded the total losses.
- Key Metrics
- Expectancy: The expectancy of 2.22 suggests that, on average, each trade generated a profit of 2.22 units.
- Maximum Drawdown: The maximum drawdown of 3.35% indicates a relatively low risk level.
- Win Rates: The win rates for both long and short positions were above 50%, suggesting effectiveness in identifying profitable opportunities.
- Breakdown of Metrics
- Profit Factor: A value of 1.38 indicates that the total profit is greater than the total loss, which is a positive indicator.
- Expectancy: A value of 2.22 indicates that on average, each trade generates a profit of 2.22, which is also a good indicator.
- Win Rate: The combination of win rates for short trades (58.74%) and long trades (67.70%) shows that this strategy is quite effective in identifying profitable opportunities.
- Largest Profit/Loss: The existence of trades with very large profits and losses indicates that this strategy has a high potential for volatility.
- Average Consecutive Wins/Losses: The average number of consecutive wins and losses provides an overview of the consistency of the strategy.
- A Closer Look at the Results
- Profitability: The strategy has demonstrated a consistent ability to generate profits, with the majority of trades resulting in positive returns.
- Potential for Large Profits: The presence of trades with exceptionally large profits indicates the strategy's potential for significant gains.
- Risk Exposure: While most losses were relatively small, the occurrence of a few large losses suggests that the strategy is not entirely risk-free.
Recommendation:
Based on the available data, this strategy has shown fairly good performance during the backtesting period. However, several points need to be considered:
- Short Backtesting Period: The backtesting period is only one month, which may not be sufficient to provide a comprehensive view of long-term performance.
- Recommendation: Extend the backtesting period to see if the results remain consistent over a longer duration.
- Market Volatility: The December 2024 period may have unique market characteristics (e.g., end-of-year, long holidays) that may not reflect general market conditions.
- Recommendation: Perform backtesting during different periods to account for varying market conditions.
- Parameter Variation: Try adjusting the indicator parameters to find the optimal combination.
- Recommendation: Experiment with different parameter settings to identify the most effective configuration.
Conclusion of Backtesting Results: The backtesting results provide a promising initial indication of the strategy'seffectiveness. However, further analysis and testing are necessary to confirm its long-termviability.
Strategy Conclusion:
The Triple Moving Average Crossover strategy is a robust method for forex traders looking to capitalize on market trends. By combining three moving averages with different periods, traders can generate more accurate signals and reduce the likelihood of false breakouts. This strategy not only helps in identifying potential entry and exit points but also provides a clearer picture of the market's overall trend. Remember to combine this strategy with proper risk management techniques to optimize trading performance.
Final Words
We hope that this article and the MQL5 Multi-Currency Expert Advisor program will be useful for traders in learning and generating new ideas, which can ultimately make money from forex trading.
Please download the Expert Advisor from My Google Drive: ExpMACross1_MCEA
If you would like to receive a source program for this article, please send a request via the Contact Us form page, and I will send it to your email, source code: ExpMACross1_MCEA
If you have any ideas for developing this EA program, please leave your comments below this article.
Thanks for reading this article.